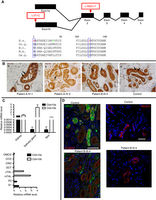
PurposeWe aimed to identify the genetic cause to a clinical syndrome encompassing hypohidrosis, electrolyte imbalance, lacrimal gland dysfunction, ichthyosis, and xerostomia (HELIX syndrome), and to comprehensively delineate the phenotype. In Aug 3, 2017, Smail Hadj-Rabia and others published an article in <> which title is “Multiplex epithelium dysfunction due to CLDN10 mutation: the HELIX syndrome”, performed homozygosity mapping, whole-genome sequencing, gene sequencing, expression studies, functional tests, protein bioinformatics, and histological characterization in two unrelated families with HELIX syndrome. Functional testing revealed that patients had a decreased NaCl absorption in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle and a severely decreased secretion of saliva. Both mutations resulted in reduced or absent Claudin-10 at the plasma membrane of epithelial cells.ConclusionCLDN10 mutations cause a dysfunction in TJs in several tissues and, subsequently, abnormalities in renal ion transport, ectodermal gland homeostasis, and epidermal integrity.
Read More