Gene ID: eg. AT5G10140, FLC
Welcome to AtMAD
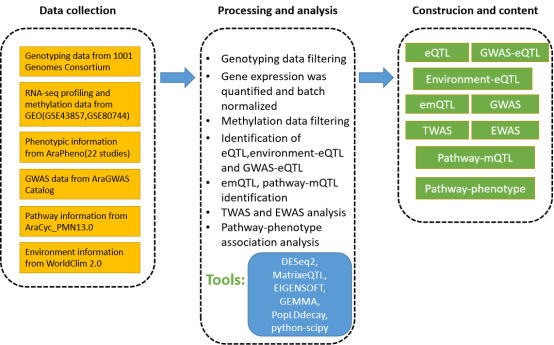
AtMAD, a public repository for large-scale measurements of genome ร transcriptome ร methylome ร pathway ร phenotype associations in Arabidopsis, designed for facilitating identification of eQTL, emQTL, pathway-mQTL, pathway-phenotype, GWAS, TWAS and EWAS. AtMAD identifies candidate variants/methylations/genes for specific phenotypes or biological processes,and provides many associations that were previously unknown in exploring biological mechanisms. All raw data comes from public free databases, including 1001 Genomes, TAIR, AraPheno, AraGWAS Catalog, AraCyc, AtPID and text mining for pubmed, etc. In AtMAD, users can: 1. Browse or search cis-eQTLs, trans-eQTLs, environment-related eQTLs and GWAS-related eQTLs in Arabidopsis(rosette leaf); 2. Browse or search methylations associated with specific genes or pathways, including emQTLs and pathway-mQTL; 3. Browse or search GWAS, TWAS and EWAS results for 462 published phenotypes curated from AraPheno; 4. Browse or search pathway-phenotype associations between AraCyc-pathways and AraPheno-phenotypes; 5. Construct Multi-omics Association Networks for visually displaying multiple association information for variants/phenotype/gene/pathway of interest and assisting researchers to understand the molecule mechanisms for multiple biological process.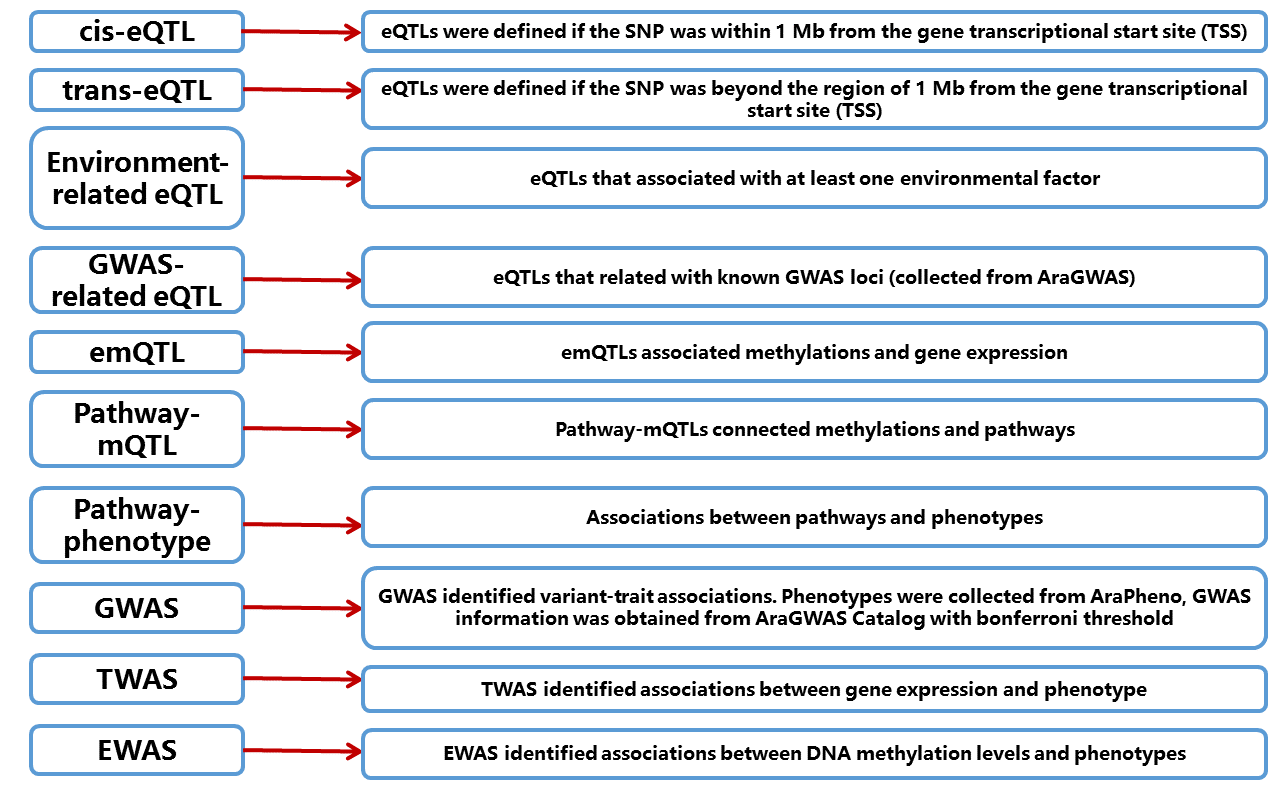 AtMAD is freely available at http://www.megabionet.org/atmad and is convenient for browsing, searching and downloading data of multi-omics associations in Arabidopsis.
Cite paper: AtMAD:ย Arabidopsis thalianaย multi-omics association databaseย
Yiheng Lan,ย Ruikun Sun,ย Jian Ouyang,ย Wubing Ding,ย Min-Jun Kim,ย Jun Wu,ย Yuhua Li,ย Tieliu Shiย Author Notes
Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 49, Issue D1, 8 January 2021, Pages D1445โD1451,ย https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa1042
AtMAD is freely available at http://www.megabionet.org/atmad and is convenient for browsing, searching and downloading data of multi-omics associations in Arabidopsis.
Cite paper: AtMAD:ย Arabidopsis thalianaย multi-omics association databaseย
Yiheng Lan,ย Ruikun Sun,ย Jian Ouyang,ย Wubing Ding,ย Min-Jun Kim,ย Jun Wu,ย Yuhua Li,ย Tieliu Shiย Author Notes
Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 49, Issue D1, 8 January 2021, Pages D1445โD1451,ย https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa1042